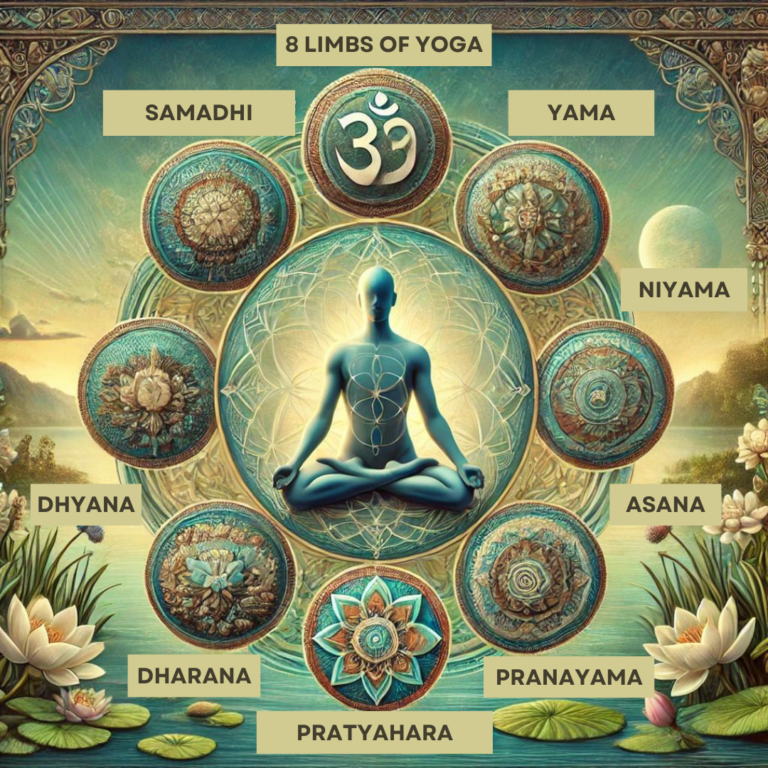
Yoga offers a holistic approach to physical and mental wellness, with asanas (poses) being an essential component. Understanding the different types of yoga asanas and their benefits will help you create a well-rounded practice that supports your health and well-being. In this article, we’ll explore five main categories of yoga asanas, their benefits, and tips on how to practice them effectively.
1. Standing Asanas
Overview:
Standing asanas lay the foundation for many yoga practices. They strengthen the legs, engage the core, and improve stability. These poses are often included at the beginning of a session to warm up the body and establish a strong base.
Examples and Benefits:
- Mountain Pose (Tadasana): The blueprint for all standing poses, Mountain Pose improves posture, strengthens the legs, and fosters a sense of grounding.
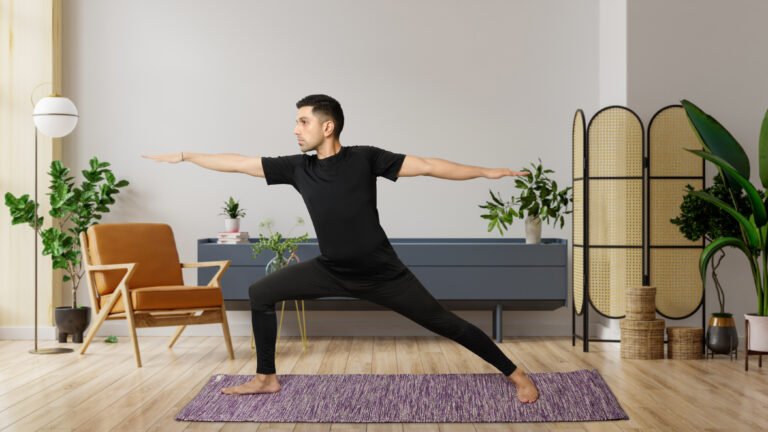
- Warrior I (Virabhadrasana I): Builds strength in the legs, arms, and shoulders while opening the chest and hips. It also enhances focus and stability.
- Triangle Pose (Trikonasana): Stretches the hips, hamstrings, and shoulders, while improving balance and opening the chest.
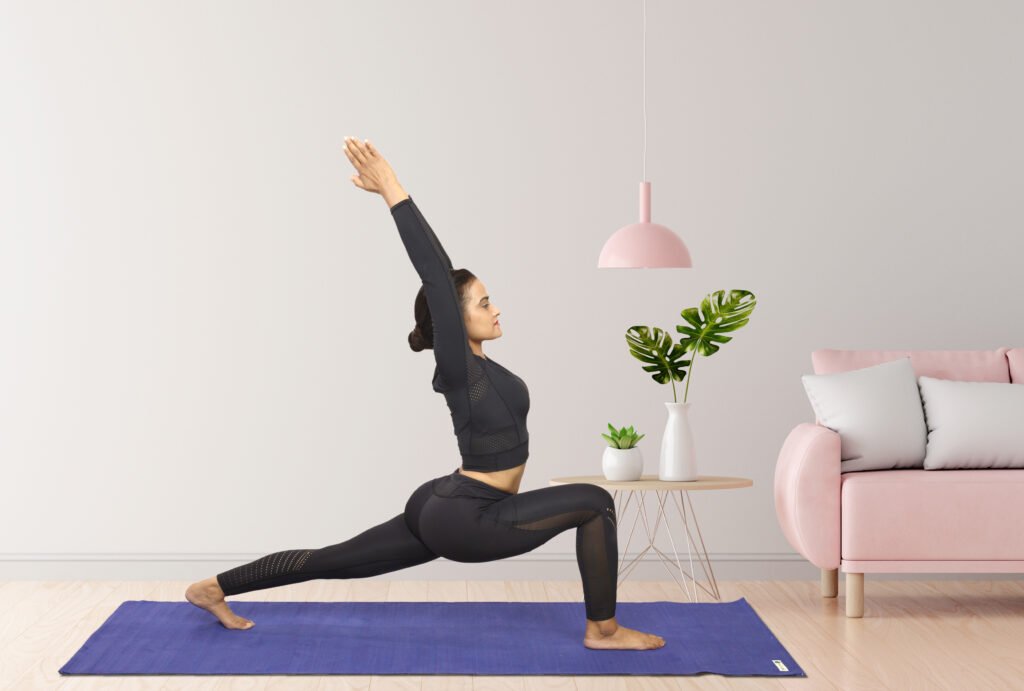

Tips for Practice:
- Root your feet firmly into the ground for stability.
- Engage your core to maintain balance and alignment.
- Focus on deep, even breathing to stay present and deepen the poses.
2. Sitting Asanas
Overview:
Sitting asanas promote relaxation and are commonly associated with meditation and breathwork. These poses stretch the legs, open the hips, and calm the mind.
Examples and Benefits:
- Easy Pose (Sukhasana): A simple cross-legged posture for meditation. It helps calm the mind and improve focus.
- Seated Forward Bend (Paschimottanasana): Stretches the spine, shoulders, and hamstrings while stimulating internal organs, making it ideal for stress relief.
- Bound Angle Pose (Baddha Konasana): Opens the hips and stretches the inner thighs, improving lower body flexibility.
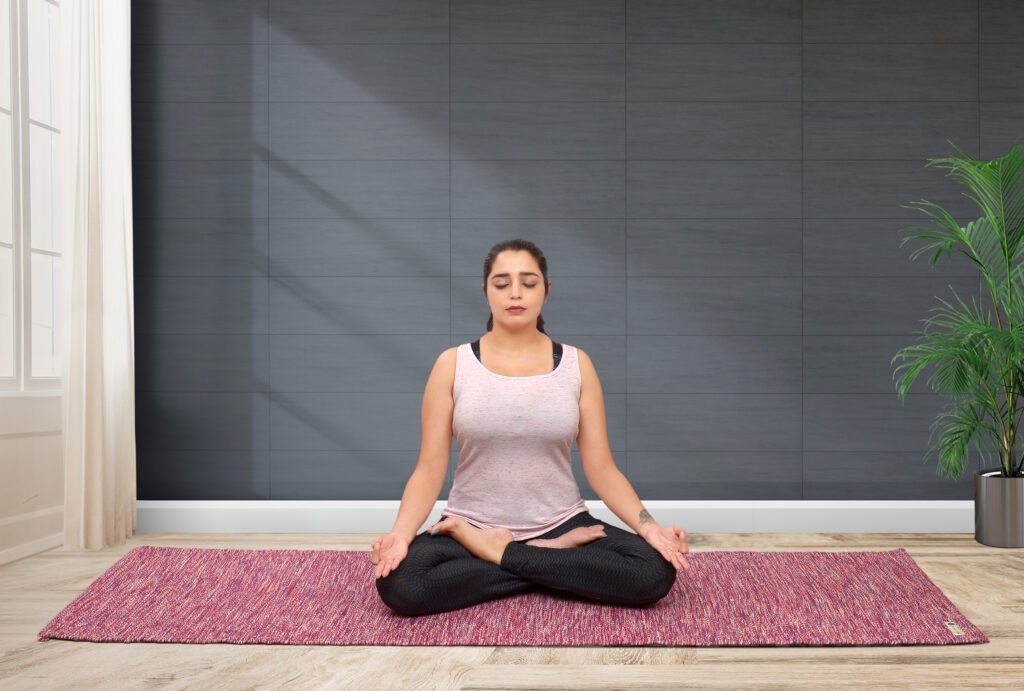

Tips for Practice:
- Sit on a folded blanket if your hips or lower back feel tight.
- Keep your spine long, avoiding slouching during forward bends.
- Use deep, slow breaths to enhance relaxation and deepen the stretches.
3. Balancing Asanas
Overview:
Balancing asanas challenge both mental focus and physical stability. These poses strengthen the core, improve coordination, and develop concentration.
Examples and Benefits:
- Tree Pose (Vrikshasana): Strengthens the legs and core, while improving balance and mental clarity.
- Eagle Pose (Garudasana): Increases flexibility in the shoulders and hips, while enhancing focus and balance.
- Half Moon Pose (Ardha Chandrasana): Strengthens the legs, improves balance, and stretches the hamstrings and chest.
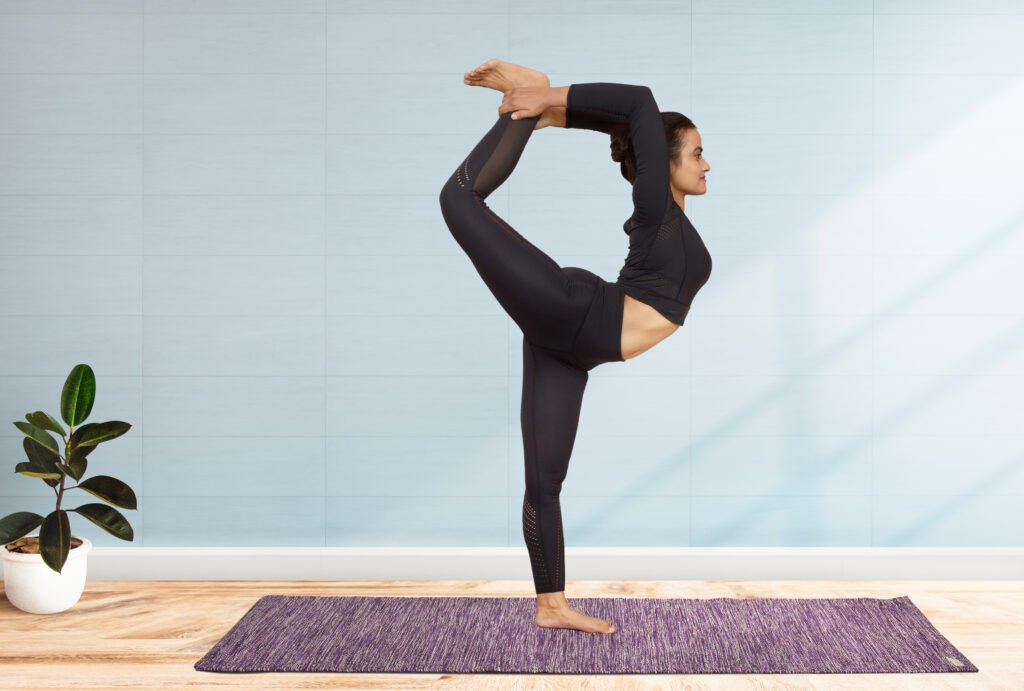

Tips for Practice:
- Fix your gaze on a single point (drishti) to help maintain balance.
- Engage your core muscles to keep your body stable.
- Practice near a wall for extra support if you’re new to balancing poses.
4. Backbends
Overview:
Backbends invigorate the body by stretching the front and strengthening the back. These poses are great for improving posture, opening the chest, and increasing spinal flexibility.
Examples and Benefits:
- Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana): Strengthens the spine while stretching the chest and shoulders. It also helps relieve stress and fatigue.
- Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana): Stretches the chest, neck, and spine while strengthening the back and legs.
- Wheel Pose (Urdhva Dhanurasana): A deep backbend that strengthens the legs, arms, and back, and boosts energy levels.

Tips for Practice:
- Warm up with gentle spinal stretches before deeper backbends.
- Lift through your chest while engaging your core to protect the lower back.
- Use props like blocks or blankets for support if needed.
5. Inversions
Overview:
Inversions, where the heart is positioned above the head, are often seen as advanced poses. They offer numerous benefits, such as improved circulation, enhanced focus, and a calming effect on the mind.
Examples and Benefits:
- Downward-Facing Dog (Adho Mukha Svanasana): Although not a full inversion, this pose stretches the entire body and strengthens the arms, shoulders, and legs.
- Shoulder Stand (Sarvangasana): Improves circulation, strengthens the shoulders and core, and helps calm the nervous system.
- Headstand (Sirsasana): Known as the “king of asanas,” Headstand strengthens the arms and core, improves balance, and sharpens mental focus.
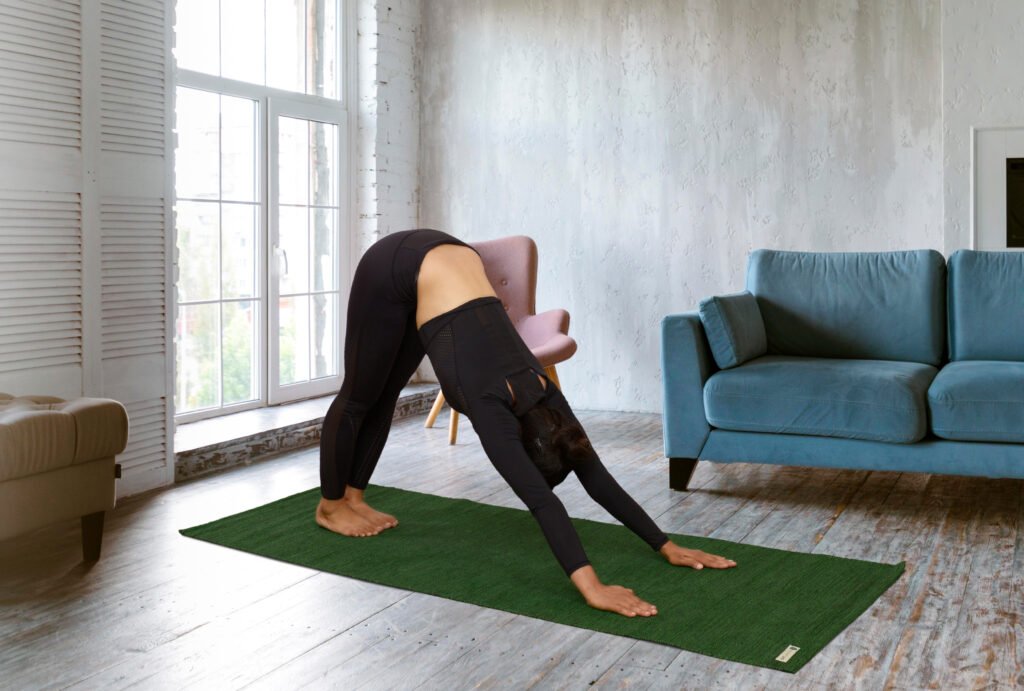

Tips for Practice:
- If you’re new to inversions, practice under the guidance of an instructor.
- Keep your core engaged to maintain control, and avoid placing too much weight on your head.
- Use a wall for support as you build strength and confidence.
Understanding the different types of yoga asanas and their benefits helps you tailor your practice to your needs. Whether you’re aiming to build strength, improve flexibility, or cultivate relaxation, incorporating a mix of these asanas will provide a balanced yoga routine that supports both physical and mental well-being.